Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) is the founding pro-survival member of the Bcl-2 protein family, exerting its pro-survival function in response to a broad range of apoptotic stimuli through the inhibition of the mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) process and the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c. [show the full text]
Bcl-2 inhibitors
Other Apoptosis Inhibitors
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Information | Product Use Citations | Product Validations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
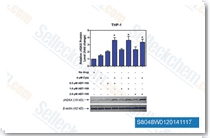
| S8048 | ABT-199 (Venetoclax) | Venetoclax (ABT-199, GDC-0199) is a Bcl-2-selective inhibitor with Ki of <0.01 nM in cell-free assays, >4800-fold more selective versus Bcl-xL and Bcl-w, and no activity to Mcl-1. Venetoclax is reported to induce cell growth suppression, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and autophagy in triple negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Phase 3. |
|
|
| S1001 | Navitoclax (ABT-263) | A potent inhibitor of Bcl-xL, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w with Ki of ", "0.5 nM, ", "1 nM and ", "1 nM in cell-free assays, Navitoclax (ABT-263) binds more weakly to Mcl-1 and A1. Phase 2. |
|

|
| S8383 | S63845 | S63845 is a new, selective MCL-1 inhibitor with the Kd value of 0.19 nM and has no discernible binding to the other Bcl-2 members, Bcl-2 or BCL-XL. |
|
|
| S1002 | ABT-737 | ABT-737 is a BH3 mimetic inhibitor of Bcl-xL, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w with EC50 of 78.7 nM, 30.3 nM and 197.8 nM in cell-free assays, respectively; no inhibition observed against Mcl-1, Bcl-B or Bfl-1. ABT-737 induces mitochondrial pathway apoptosis and Mitophagy. Phase 2. |
|

|
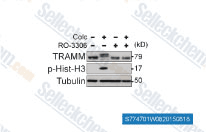
| S7747 | Ro-3306 | RO-3306 is an ATP-competitive, and selective CDK1 inhibitor with Ki of 20 nM, >15-fold selectivity against a diverse panel of human kinases. RO-3306 enhances p53-mediated Bax activation and mitochondrial apoptosis. |
|
|
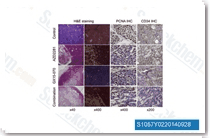
| S1057 | Obatoclax Mesylate (GX15-070) | Obatoclax Mesylate (GX15-070) is an antagonist of Bcl-2 with Ki of 0.22 μM in a cell-free assay, and can assist in overcoming MCL-1 mediated resistance to apoptosis. |
|
|
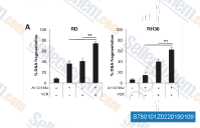
| S7801 | A-1331852 | A-1331852 is a potent and selectiveBCL-XL inhibitor with Ki value less than 0.01 nM for BCL-XL and 6 nM, 4 nM, 142 nM for Bcl-2, Bcl-W, MCL-1 respectively. It may be useful in the treatment of cancer, immune and autoimmune diseases. |
|
|
| S7790 | A-1210477 | A-1210477 is a potent and selective MCL-1 inhibitor with Ki and IC50 of 0.454 nM and 26.2 nM, respectively, >100-fold selectivity over other Bcl-2 family members. |
|
|
| S1121 | TW-37 | TW-37 is a novel nonpeptide inhibitor to recombinant Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 with Ki of 0.29 μM, 1.11 μM and 0.26 μM in cell-free assays, respectively. |
|
|
| S7800 | A-1155463 Dihydrochloride | A-1155463 Dihydrochloride, a highly potent and selective BCL-XL inhibitor, shows picomolar binding affinity to BCL-XL, and >1000-fold weaker binding to BCL-2 and related proteins BCL-W(Ki=19 nM) and MCL-1(Ki>440 nM). |
|
|
Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) is encoded by the Bcl-2 gene and is the first identified member of a large family of apoptosis regulatory proteins (Bcl-2 family) that derives its name from the B-cell lymphoma 2, as it is the second member of a variety of proteins initially described in the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation in human follicular B-cell lymphomas. Bcl-2 contains four Bcl-2 homology domains (BH1-BH4) that mediate the formation of homodimer and heterodimer with relative proteins such as Bax, Bad, Bak and Bcl-xL, and a trans-membrane (TM) domain that mediates insertion into the outer membrane of the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Bcl-2 proteins are generally integrated within the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), and may also be in the cytosol or ER membrane. The Bcl-2 and other antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family preserve the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) integrity, thus inhibiting the mitochondrial signaling pathway of apoptosis, by complex interactions with the proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins such as Bax, Bak, Bim, Puma and tBid. [1][2]
Bcl-2 suppresses apoptosis in response to a broad range of stress stimuli, including those frequently encountered during tumor development, such as oncogene activation, DNA damage, hypoxia (oxygen deprivation), loss of appropriate growth signals and anoikis (loss of cell attachment). In healthy cells, Bax and Bak are kept in check by the pro-survival Bcl-2 family members and the binding of BH3-only proteins unleashes Bax/Bak. Bcl-2 is also critical for the survival of renal epithelial stem cells during embryogenesis, melanocyte progenitors and mature B and T lymphocytes. Bcl-2 over-expression accelerates Eu-myc-induced lymphomagenesis, but loss of endogenous Bcl-2 does not prevent or delay Eu-myc-induced B lymphoma development. Bcl-2 proteins also constitutively binds to Beclin-1, and its dissociation through post-translational modification of Beclin-1 and/or Bcl-2 proteins such as phosphorylation by JNK1, or direct competition for the Bcl-2 BC groove by another BH3-only protein such as Bad, may be sufficient to induce autophagy, leading to the suggestion that autophagy and apoptosis are mechanistically linked. Single-site phosphorylation at Serine 70 (S70) is required for the antiapoptotic function of Bcl-2, and multisite phosphorylation at Threonine 69, S70, and S87 has been reported to inactivate Bcl-2. Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 has been shown to enhance activity to allow response to extracellular growth-factor-mediated signals. [1][2][3]
In addition, Bcl-2 is over-expressed in human follicular centre B-cell lymphoma; high levels of Bcl-2 are also detected in significant numbers of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), DLBCL and mantle cell lymphoma, as well as in certain solid tumours(brain, breast and lung). The upregulation of Bcl-2 in CLL and other cancers has been attributed to the hypo-methylation of the Bcl-2 promoter or, possibly more importantly due to hemizygous or homozygous loss of the micro RNAs (miRs) 15a and 16-1 that negatively regulate Bcl-2. The dysregulated Bcl-2 proteins in cancer can lead to increased survival of abnormal cells, which are thought to be involved in resistance to conventional cancer treatment. Mice that constitutively express both Myc and Bcl-2 transgenes develop lymphoblastic leukaemia with high incidence, while shut-down of the inducible Bcl-2 transgene in lymphoma-burdened bi-transgenic mice results in tumor regression and significantly prolonged animal survival in many cases, indicating that inactivation of Bcl-2 constitutes a promising new approach to cancer therapy. Small molecule mimetics of BH3-only proteins that can directly target pro-survival Bcl-2 family members are being developed as a novel therapeutic approach. ABT-737 and the closely related orally bioavailable ABT-263, belong to the BH3 mimetic small molecule inhibitors, targeting Bcl-2 and Bcl-2-related proteins such as Bcl-xL and Bcl-w, therefore promoting tumor regression in murine xeno-transplanation models of certain human lymphomas or small cell lung carcinomas and in primary patient-derived follicular lymphoma cells. [1][4]
