| S2782 |
GW4064
|
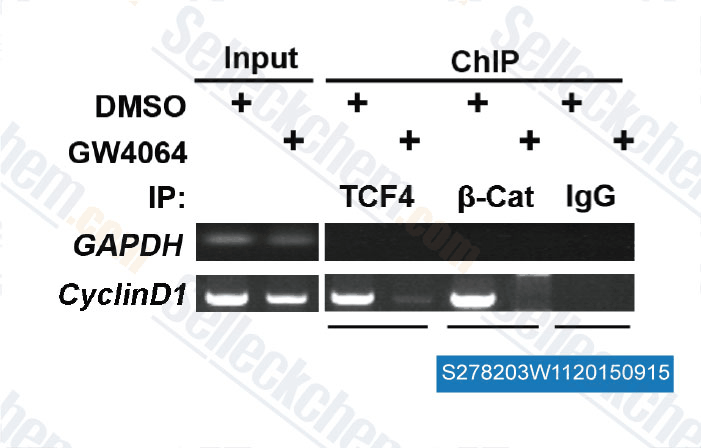
GW4064 is an agonist of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) with EC50 of 65 nM in CV1 cell line and displays no activity at other nuclear receptors at concentrations up to 1 μM. This compound stimulates Autophagy in MCF-7 cells.
|
-
Life Metab, 2025, 4(2):loaf004
-
Gut Microbes, 2024, 16(1):2379566
-
Mol Metab, 2024, 79:101841
|
|
| S7660 |
Obeticholic Acid (INT-747)
|
Obeticholic Acid (INT-747) is a potent and selective farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist with EC50 of 99 nM, and it inhibits autophagy. This compound is in Phase 3.
|
-
Nat Commun, 2025, 16(1):2093
-
Cell Commun Signal, 2025, 23(1):236
-
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2025, 328(5):G558-G577
|
|
| S2694 |
Turofexorate Isopropyl (XL335)
|
Turofexorate Isopropyl (XL335, Fxr 450) is a potent, selective FXR agonist with EC50 of 4 nM, highly selective versus other nuclear receptors, such as LXR, PPAR, ER and etc. Phase 1.
|
-
Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(15):1784-1797
-
Oncotarget, 2015, 6(6):4226-38
-
Placenta, 2015, 36(5):545-51
|
|
| S1843 |
Chenodeoxycholic Acid
|
Chenodeoxycholic Acid (Chenodiol, Chenodesoxycholic acid, Chenocholic acid,CDCA) is a naturally occurring human bile acid, and inhibits production of cholesterol in the liver and absorption in the intestines. This compound is a hydrophobic primary bile acid that activates nuclear receptors (FXR) involved in cholesterol Metabolism.
|
-
Acta Pharm Sin B, 2024, 14(8):3513-3527
-
World J Gastroenterol, 2024, 30(5):485-498
-
Food Funct, 2021, 10.1039/d1fo01272j
|
|
| S4003 |
Lithocholic acid
|
Lithocholic acid is a toxic secondary bile acid, causes intrahepatic cholestasis, has tumour-promoting activity, its toxic effect can be protected after it activates the vitamin D receptor, PXR and FXR.
|
-
FEBS Open Bio, 2023, 13(9):1789-1806
-
Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 149:112825
-
Hum Mol Genet, 2020, ddaa244
|
|
| S6413 |
fexaramine
|
fexaramine is a potent, selective farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist with an EC50 of 25 nM and it displays no activity at hRXRα, hPPARα, hPPARγ, hPPARδ, mPXR, hPXR, hLXRα, hTRβ, hRARβ, mCAR, mERRγ and hVDR receptors.
|
-
Mol Med, 2025, 31(1):258
|
|
| S0033 |
BAR502
|
BAR502 (Compound 30) is a dual FXR and GPBAR1 agonist with IC50 values of 2 μM and 0.4 μM, respectively.
|
|
|
| S0037 |
Nidufexor (LMB-763)
|
Nidufexor (LMB-763) is an agonist of farnesoid X receptor (FXR).
|
|
|
| S8733 |
Tropifexor (LJN452)
|
Tropifexor (LJN452) is a novel and highly potent agonist of FXR with EC50 of 0.2 nM in HTRF assay. This compound shows no significant off-target activity against a broad panel of enzyme, ion channel, nuclear receptor, and GPCR (>10000-fold selectivity for FXR).
|
|
|
| S0874 |
Vonafexor (EYP001)
|
Vonafexor (EYP001, PLX007) is a novel non-bile acid, selective, second generation farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist.
|
|
|
| S6547 |
Cilofexor (GS-9674)
|
Cilofexor (GS-9674) is a potent, selective oral agonist of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) with an EC50 of 43 nM. It has demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic effects, and reduced portal pressure in preclinical liver fibrosis models, showing potential therapeutic benefit for primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) research.
|
|
|
| E5874New |
INT-767
|
INT-767 is a dual agonist of farnesoid X receptor (FXR)/TGR5 with an EC50 of 0.033 μM and 0.67 μM, respectively. It significantly improves serum liver enzymes, hepatic inflammation, and biliary fibrosis, while inducing bile flow and biliary HCO₃⁻ output, making it a promising tool for chronic cholangiopathy research.
|
|
|
| S0403 |
LY2562175
|
LY2562175 is a potent and selective agonist of FXR. This compound promotes transcriptional activation of human FXR in a cell-based cotransfection assay with EC50 of 193 nM.
|
|
|
| S7076 |
T0901317
|
T0901317 is a potent and selective agonist for both LXR and FXR, with EC50 of 20nM for LXR
and 5
M for FXR, respectively. This compound is a dual inverse agonist of ROR
and ROR
with Ki of 132 nM and 51 nM, respectively. It significantly suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis.
|
-
J Clin Invest, 2025, 135(10)e186478
-
J Exp Med, 2025, 222(3)e20230647
-
Neurobiol Dis, 2025, 215:107094
|

|




