research use only
Macitentan Endothelin Receptor antagonist
Cat.No.S8051
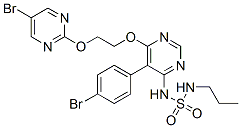
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 588.27
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CXCR Hedgehog/Smoothened PKA Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor Histamine Receptor Dopamine Receptor Ras KRas |
|---|---|
| Other Endothelin Receptor Inhibitors | BQ-123 Zibotentan (ZD4054) Sparsentan (PS-433540, RE-021) Carperitide Acetate Lu-135252 Pearl Extract Aprocitentan Atrasentan |
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 588.27 | Formula | C19H20Br2N6O4S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 441798-33-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | ACT 064992 | Smiles | CCCNS(=O)(=O)NC1=C(C(=NC=N1)OCCOC2=NC=C(C=N2)Br)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Br | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(169.98 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ET-A
0.5 nM
ET-B
391 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Macitentan achieves full inhibition of intracellular calcium increase induced by ET-1 on primary human pulmonary smooth muscle cells with approximate IC50 of 1 nM. This compound inhibits ET-1-induced contractions on isolated rat aortic rings or S6c-induced contractions on isolated rat tracheal rings with pA2 of 7.6 and 5.9, respectively.
|
| In vivo |
Macitentan administered to normotensive rats, increases plasma ET-1 concentration, which occurred at a 10-fold lower dose than with bosentan. This compound dose-dependently decreases mean arterial blood pressure in hypertensive DOCA-salt rats with a maximal effect of -26 mm Hg at a dose of 10 mg/kg and a ED50 of 1mg/kg. At the maximal effective dose, the duration of the blood pressure response to this compound is approximately 40 hr. It orally administrated dose-dependently prevents the development of pulmonary hypertension and the development of right ventricle hypertrophy with a maximal efficacy of 30 mg/kg/day in monocrotaline rat model of pulmonary hypertension. Chronic oral administration of this chemical at 30 mg/kg/day significantly improves the 42-day survival in monocrotaline rats (83 vs 50% survival in macitentan vs vehicle; 66% reduction of mortality at 42 days).
This compound (30 mg/kg/day) treated for 24 h partially prevents the development of renal vasoconstriction and increases renal blood flow in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. It increases glomerular filtration rate and decreases filtration fraction, and attenuates vascular and tubulo-interstitial lesions and also glomerular damage.
This chemical (25 mg/kg/day, p.o.) attenuates the increase of renal, cardiac and retinal ET-1, TGF-β1, VEGF, FN, EDB+FN, collagenα-I(IV) mRNA expression along with increased FN, collagen protein and NF-κB activation induced by type 2 diabetes in db/db mice. It also ameliorates mesangial expansion, cardiac dysfunction and the increased expression of ANP and BNP in these diabetic mice.
This compound (100mg/kg) treatment combined with paclitaxel (5 mg/kg) reduced tumour incidence (5/9 vs 9/9 of paclitaxel along) and further reduces tumour weight (median [range]: 0.1 vs 0.4 g of paclitaxel along) and incidences of ascites (0/9 vs 4/9 of paclitaxel along) in SKOV3ip1 ovarian cancer model when compared with paclitaxel alone. It plus paclitaxel inhibits the phosphorylation of ETRs and suppresses the survival pathways of tumour cells by decreasing the levels of pVEGFR2, pAkt, and pMAPK. This chemical enhances effects of paclitaxel on tumour cells dividing (Brud+ cells: 18.5 vs 30.8 of paclitaxel along) and apoptosis (TUNEL+ cells: 195 vs 150 of paclitaxel along).
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05731492 | Recruiting | Arterial Hypertension Pulmonary |
Actelion |
March 14 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05167825 | Recruiting | Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension |
Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. |
November 14 2022 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05433675 | Completed | Healthy |
Actelion |
June 22 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05392530 | Completed | Healthy |
Actelion |
May 25 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05373108 | Completed | Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy |
University of California Los Angeles|American Heart Association|Janssen LP |
May 19 2022 | Phase 4 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
