research use only
Enalaprilat Dihydrate RAAS inhibitor
Cat.No.S1657
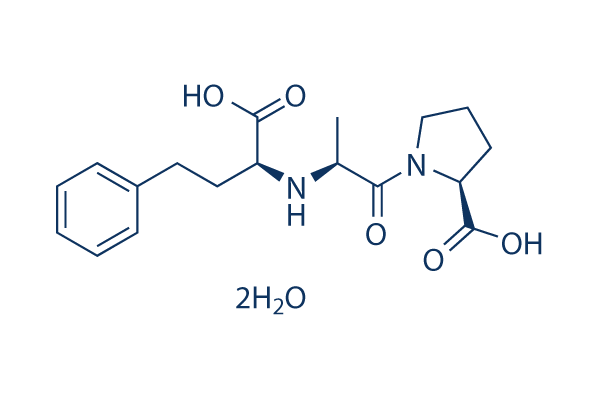
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 348.4
Quality Control
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 348.4 | Formula | C18H24N2O5.2H2O |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 84680-54-6 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | MK-422 Dihydrate | Smiles | CC(C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)O)NC(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)O.O.O | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 70 mg/mL
(200.91 mM)
Water : 5 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
The 1st dicarboxylate-containing ACE inhibitor developed to overcome captopril limitations.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ACE
1.94 nM
|
| In vitro |
Enalaprilat has high affinity for human endothelial ACE with IC50 of 1.94 nM in vitro binding assay by displacing a saturating concentration of [125I]351A, a radiolabeled lisinopril analogue from ACE binding sites, and shows bradykinin/angiotensin I selectivity ratio of 1.00 calculated from double displacement experiments. Enalaprilat has the strong inhibitory effect on Aβ42-to-Aβ40-converting activity found in the N-domain of ACE, exhibiting a 10-fold lower IC50 (0.003~0.01 μM) than captopril (0.03~0.1 μM). Enalaprilat (100 nM) blocks protein kinase C epsilon by directly activating bradykinin B1 receptor at the canonical Zn2+ binding site, leading to prolonged nitric oxide (NO) production in cytokine-treated human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Enalaprilat attenuates the IGF-I induced neonatal rat cardiac fibroblast growth (30% reduction) in a concentration-dependent fashion, with IC50 of 90 mM.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Single displacement binding assay
|
|
The binding assay is based on the competitive displacement of [125I]351A by Enalaprilat performed on whole endothelial cells. Subconfluent HUVECs in 6-well plates are rinsed with 2 mL binding buffer (140 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 1.03 mM MgCl2, 0.42 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM HEPES, 2 mM sodium pyruvate and 5 mM glucose, pH 7.4), and the culture medium is replaced with 2.5 mL fresh binding buffer containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The Enalaprilat (2.5-12.5 μL, 0.1-50 nM) or equivalent volumes of diluent are added to the binding buffer. A saturating amount of [125I]351A (10 μL, typically 106 cpm) is then added to each sample and the plates are incubated at 37 °C for 2 hours in a thermostatic bath. The cells are then rinsed twice with 1.5 mL binding buffer. Finally, the cells are extracted with 0.5 mL NaOH 1 N, incubated for 5 minutes, and the radioactivity is counted with a gamma counter. The ratio of specific [125I]351A bound to total bound activity (B/B0) is calculated, and the inhibitory potency of Enalaprilat expressed as the concentration of ACE inhibitors able to displace 50% of the bound radioligand, i.e. the IC50.
|
|
| In vivo |
Enalaprilat has unfavourable ionisation characteristics to allow sufficient potency for oral administration, thus Enalaprilat is only suitable for intravenous administration, which is overcome by the esterification with ethanol to produce Enalapril. Administration of Enalaprilat induces a significant reduction of MAP at 70 minutes compared with the placebo group during haemorrhagic shock in rats, and results in a 50% reduction of CO, a general tendency of EB extravasation which is significant in the kidney and lungs, and a significant increase in ileal EB extravasation (53%). Enalaprilat has no effect in nonhypertrophied hearts, but significantly attenuates the greater increase in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure in hypertrophied hearts compared with no drug.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03051282 | Active not recruiting | Healthy Volunteers |
University of Michigan |
April 1 2017 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02654678 | Unknown status | Heart Failure|Dilated Cardiomyopathy|Congenital Heart Disease |
Ethicare GmbH |
March 2016 | Phase 2|Phase 3 |
| NCT02652728 | Unknown status | Heart Failure|Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
Ethicare GmbH |
January 2016 | Phase 2|Phase 3 |
| NCT02652741 | Unknown status | Heart Failure|Congenital Heart Disease |
Ethicare GmbH |
January 2016 | Phase 2|Phase 3 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
