research use only
Dexrazoxane HCl Topoisomerase inhibitor
Cat.No.S1222
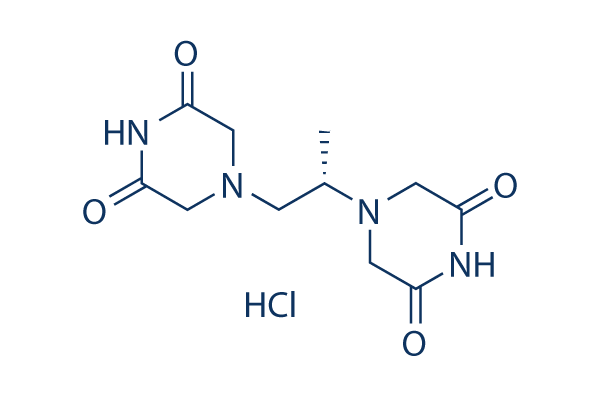
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 304.73
Quality Control
| Related Targets | HDAC PARP ATM/ATR DNA-PK WRN DNA/RNA Synthesis PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase eIF |
|---|---|
| Other Topoisomerase Inhibitors | Camptothecin (CPT) Betulinic acid Beta-Lapachone (S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Amonafide Voreloxin (SNS-595) hydrochloride Ellagic acid Cu(II)-Elesclomol Hydroxy Camptothecine Rubitecan |
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 304.73 | Formula | C11H16N4O4.HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | 3 years -20°C powder (seal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 149003-01-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | ADR-529 HCl, ICRF-187 HCl | Smiles | CC(CN1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1)N2CC(=O)NC(=O)C2.Cl | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 61 mg/mL
(200.17 mM)
Water : 61 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Topo II
(Cell-free assay) |
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Dexrazoxane (10 mM), known clinically to limit anthracycline cardiac toxicity, prevents daunorubicin-induced myocyte apoptosis, but not necrosis induced by higher anthracycline concentrations in rat cardiac myocytes. Dexrazoxane presumably exerts its cardioprotective effects by either binding free or loosely bound iron, or iron complexed to doxorubicin, thus preventing or reducing site-specific oxygen radical production that damages cellular components. Dexrazoxane specifically abolishes the DNA damage signal gamma-H2AX induced by doxorubicin, but not camptothecin or hydrogen peroxide, in H9C2 cardiomyocytes. Dexrazoxane also induces rapid degradation of Top2beta, which parallels the reduction of doxorubicin-induced DNA damage. Dexrazoxane antagonizes doxorubicin-induced DNA damage through its interference with Top2beta, which could implicate Top2beta in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Dexrazoxane is hydrolyzed to its active form intracellularly and binds iron to prevent the formation of superhydroxide radicals, thus preventing mitochondrial destruction. |
| In vivo |
Dexrazoxane combined with doxorubicin, daunorubicin, or idarubicin reduces the tissue lesions in B6D2F1 mice (expressed as area under the curve of wound size times duration) by 96%, 70%, and 87%, respectively. Dexrazoxane combined with doxorubicin, daunorubicin, or idarubicin results in a statistically significant reduction in the fraction of mice with wounds as well as the duration of wounds. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-Chk1 / Chk1 / p-Chk2 / ChK2 ATF3 / TOP2A TOPOIIα / TOPOIIβ / TOPO I / PABP2 |
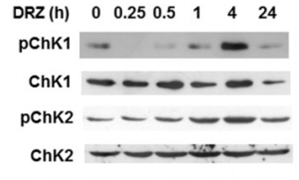
|
25521189 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
